Description
Contemporary home with terrace and backyard Escazu Jaboncillos
Contemporary home with terrace and backyard Escazu.
Located in Escazu, Jaboncillo, one of the most prestigious neighborhoods.
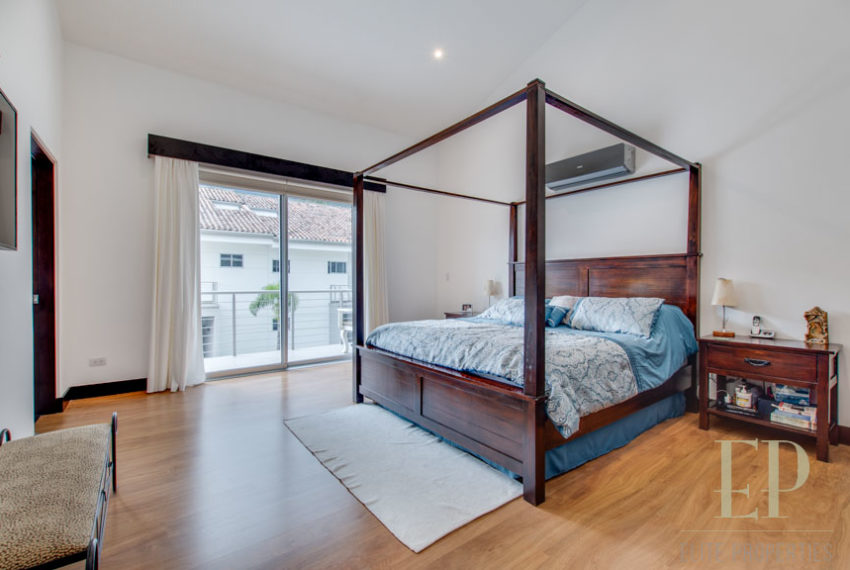
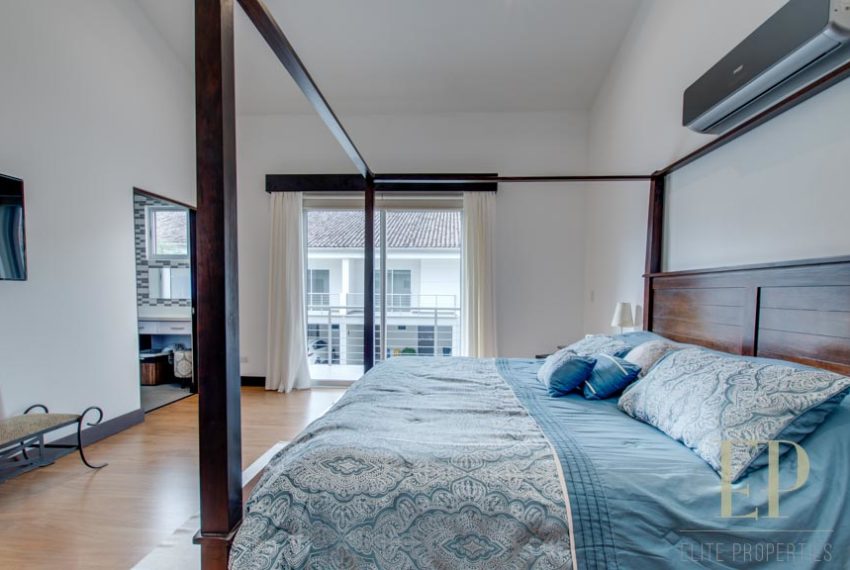
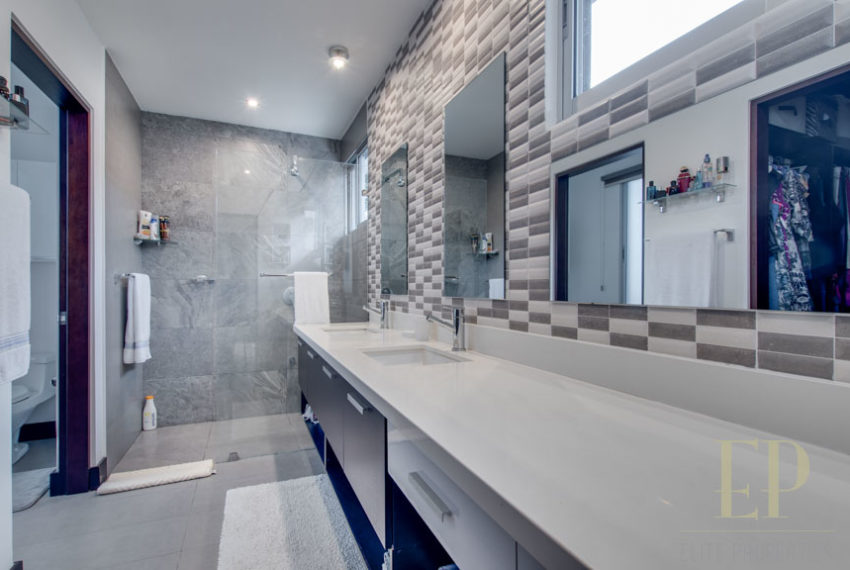
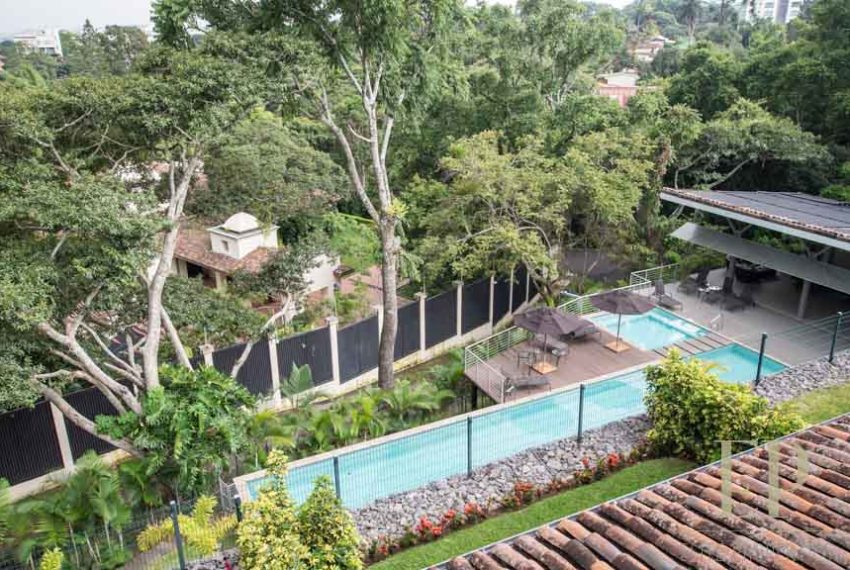
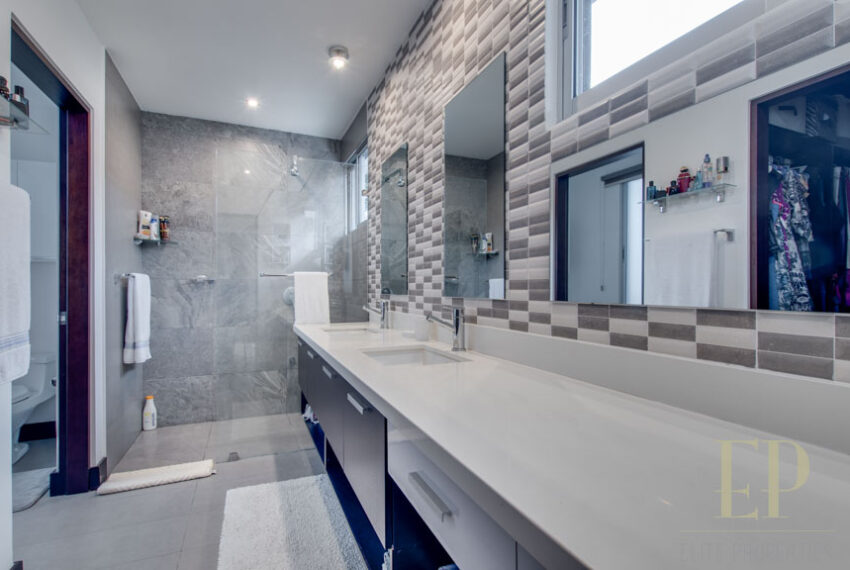
Condominium with Swimming pool, gym, security 24/7. This beautiful house has not only one of the best views in the condominium but also many upgrades. Extra cabinet spaces, storage, gas installation, A/C in the bedrooms, double sink in master bathroom.
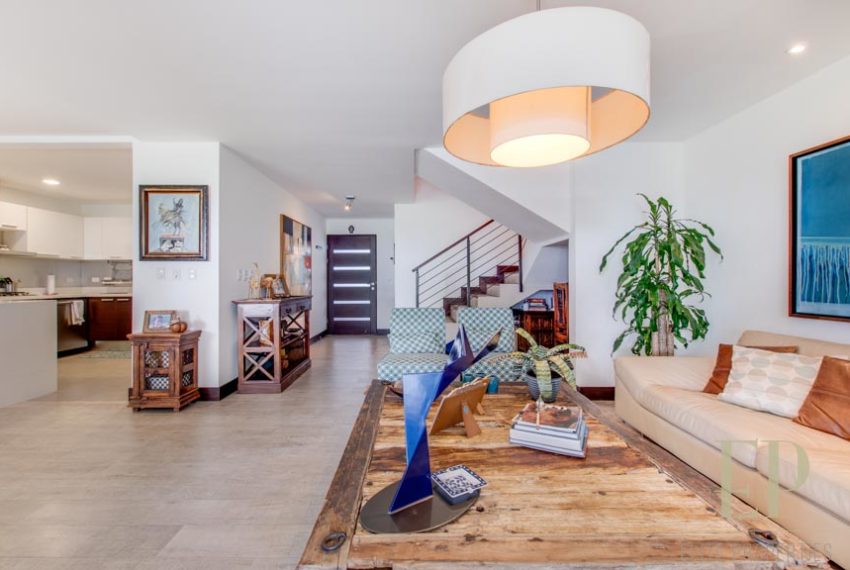
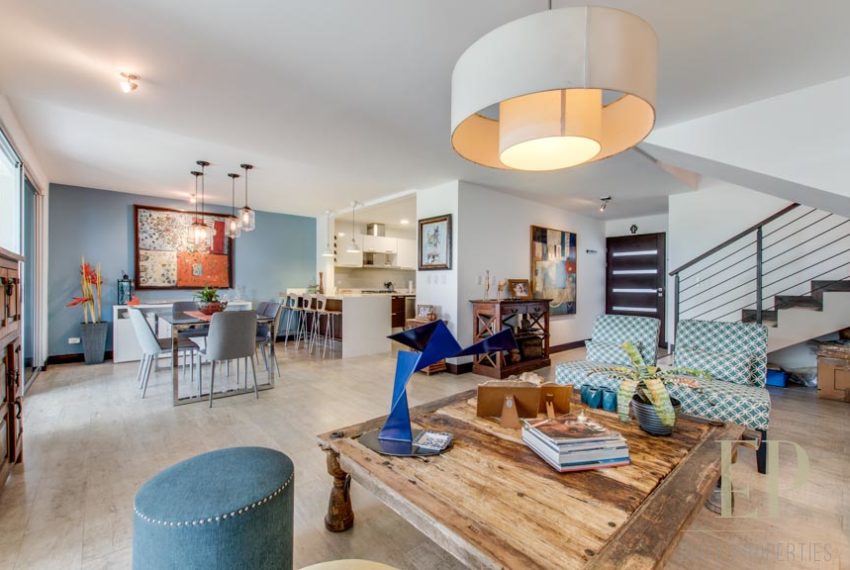
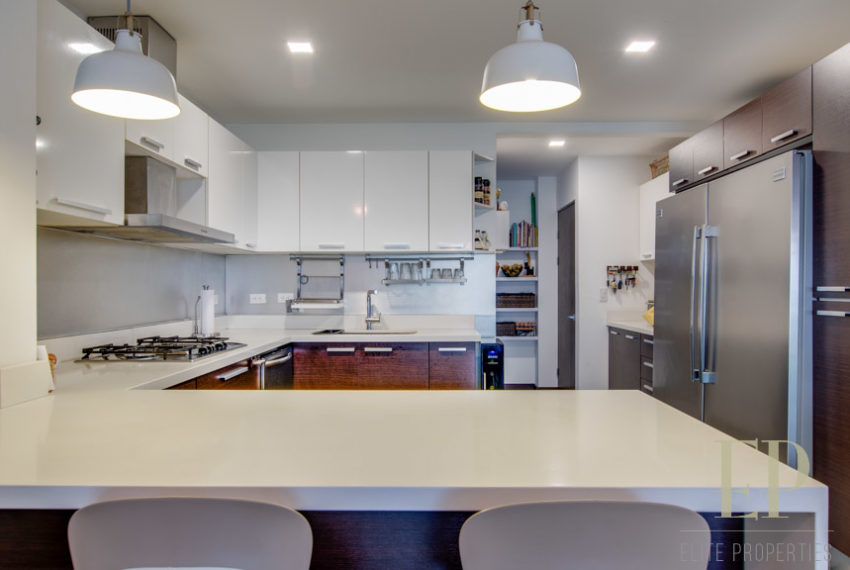
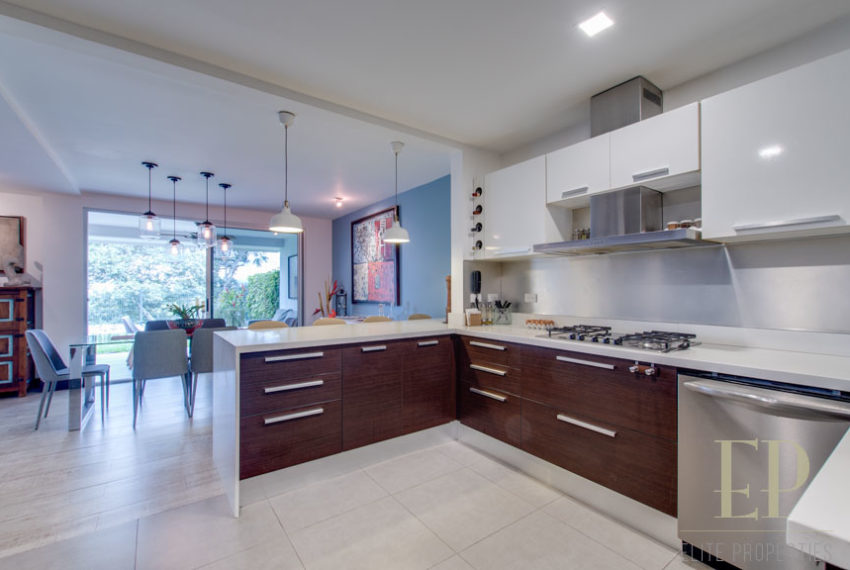
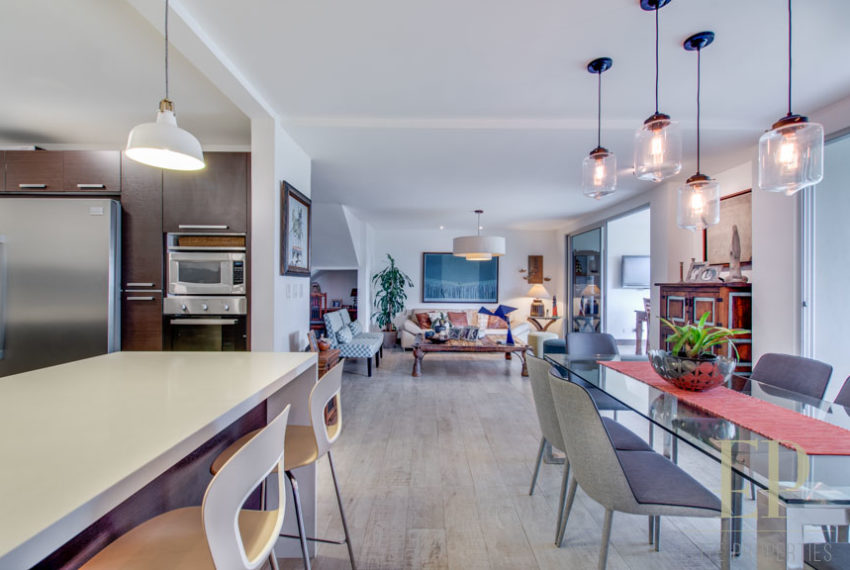
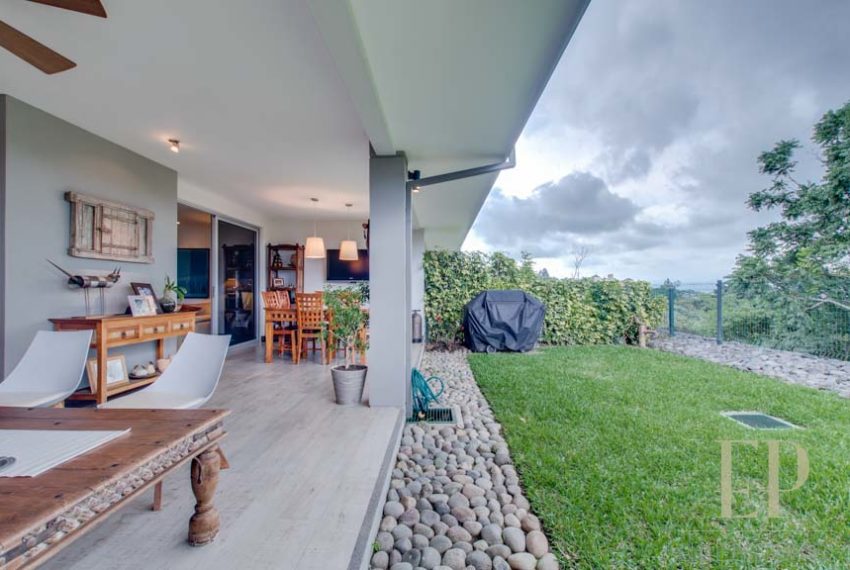
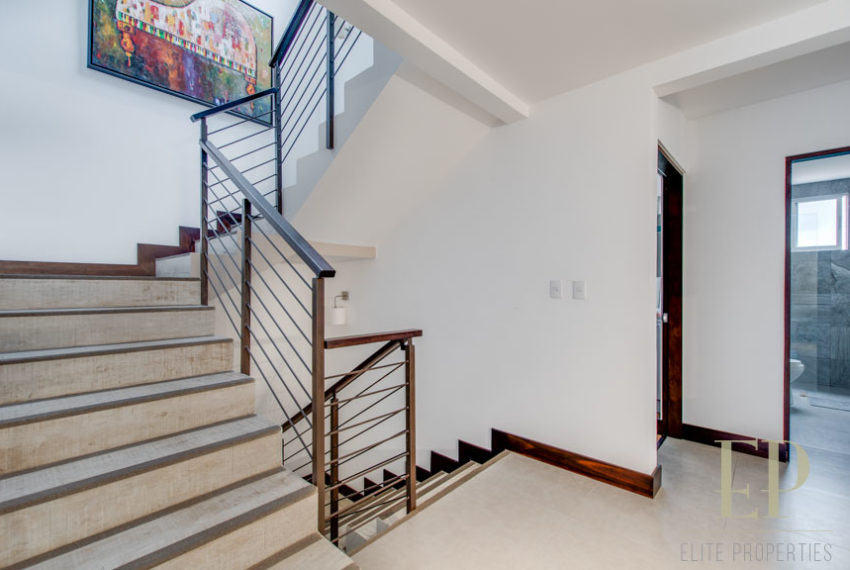
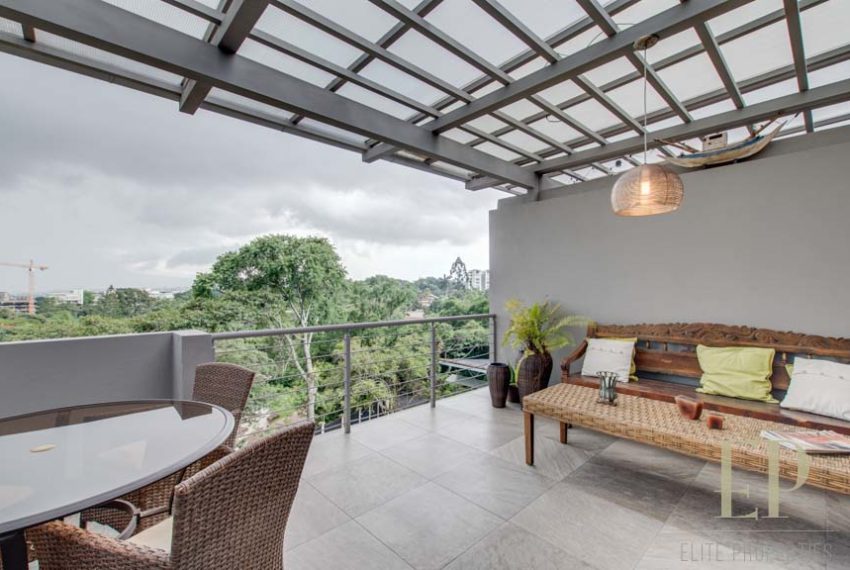
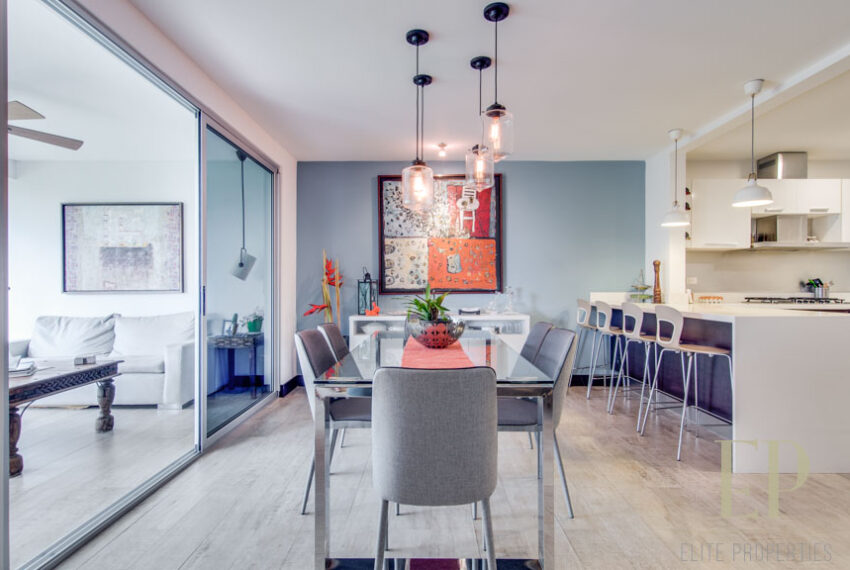
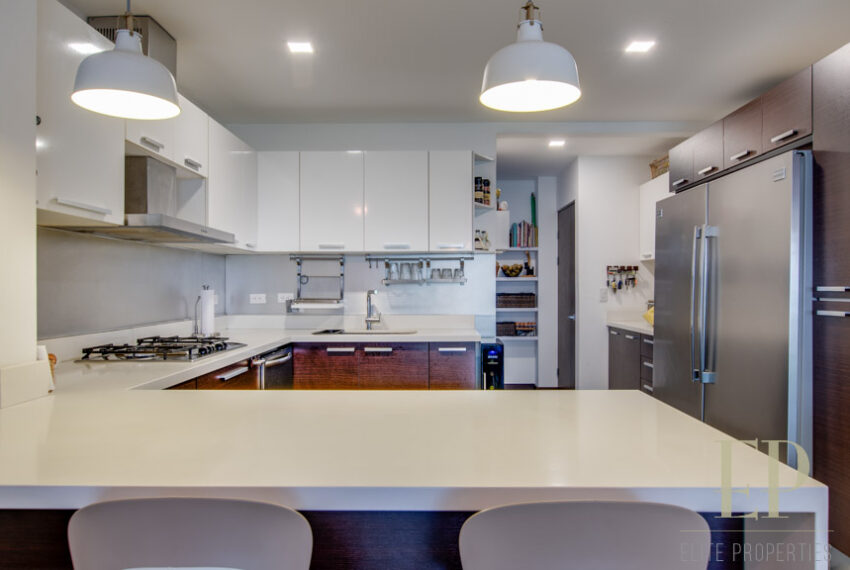
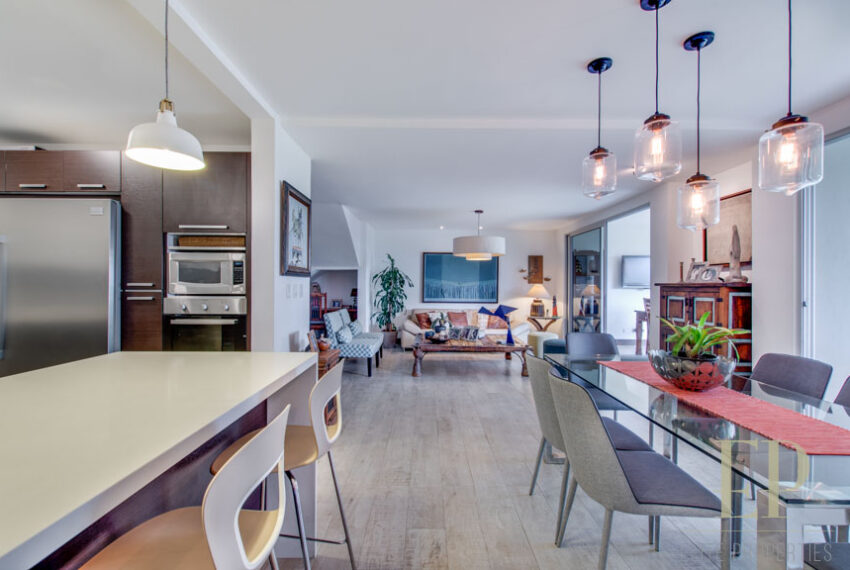
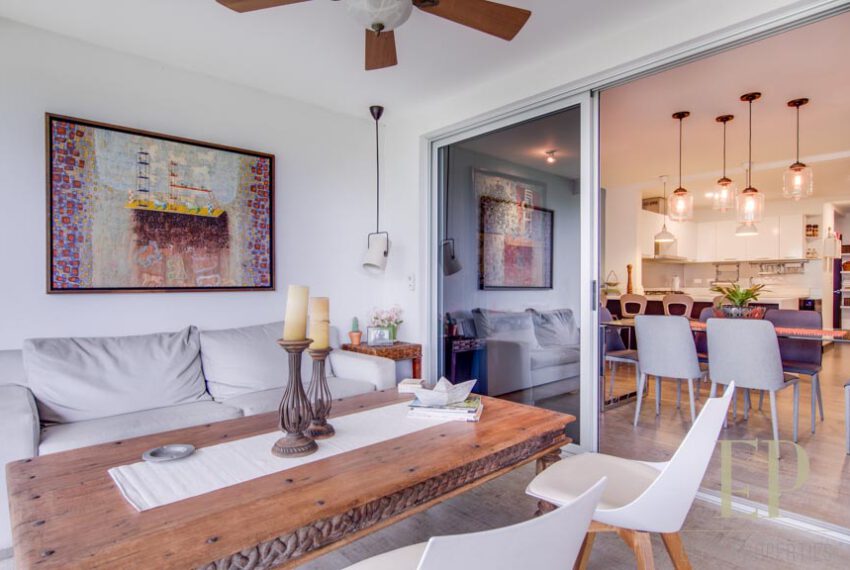
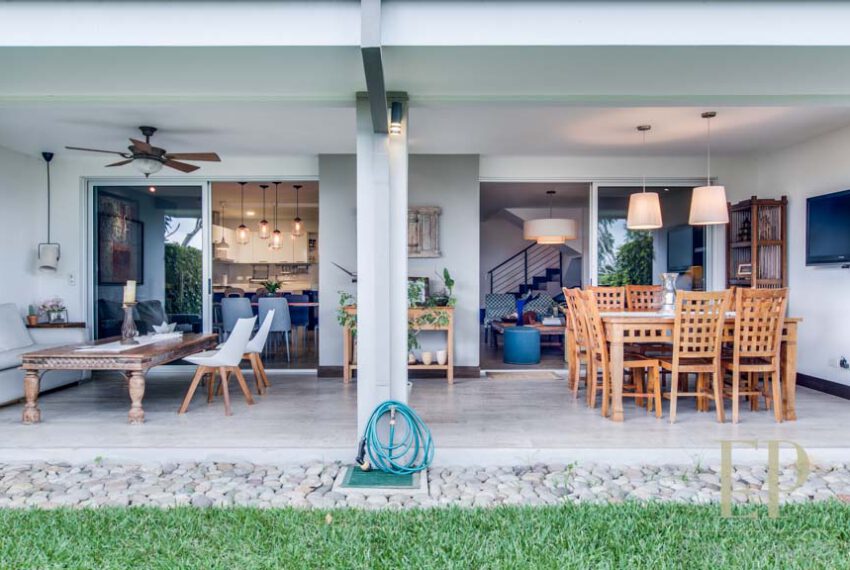
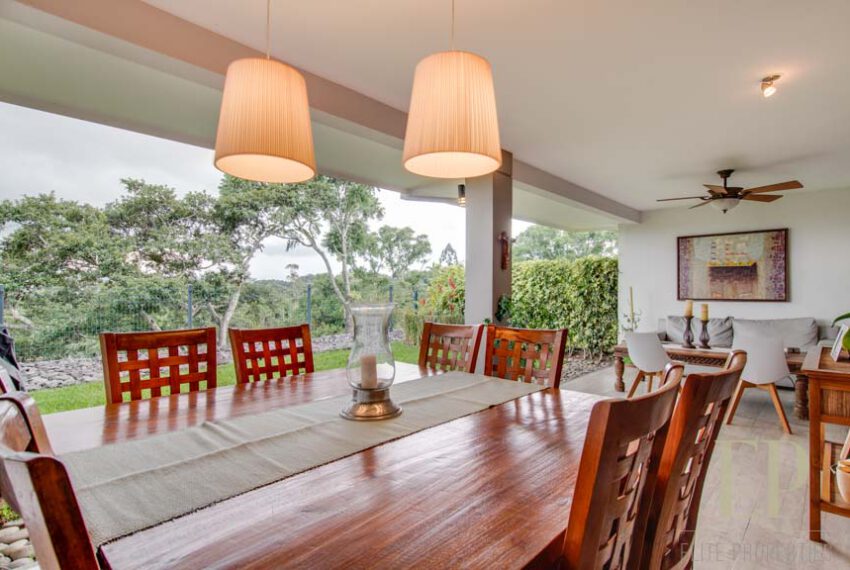
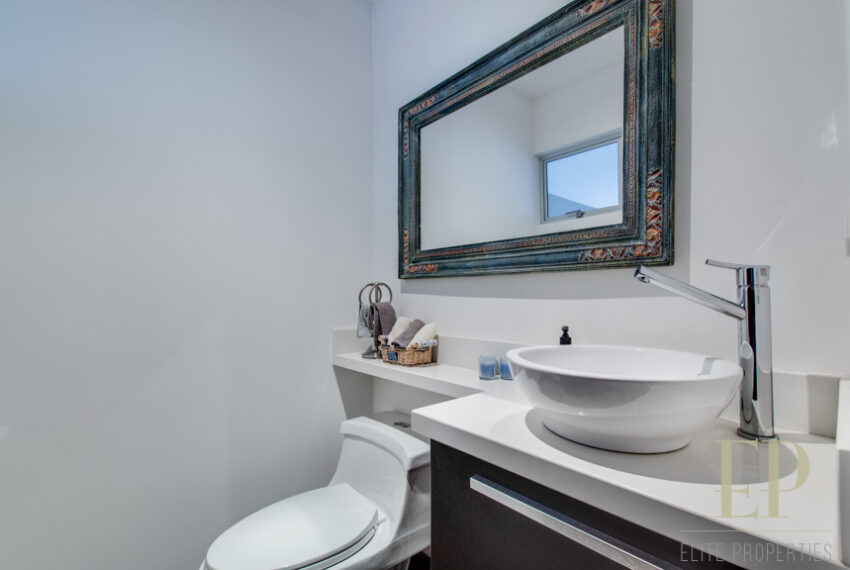
THREE STORIES CONTAIN: First floor: ample living, dining space with open kitchen, comfortable terrace and green patio with views. Maid’s room with bathroom, garage for 3 cars, guest bathroom.
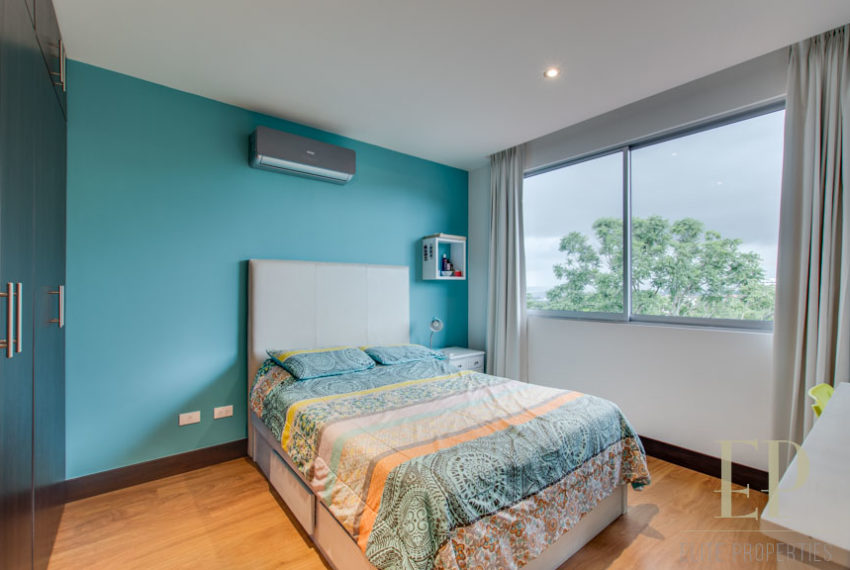
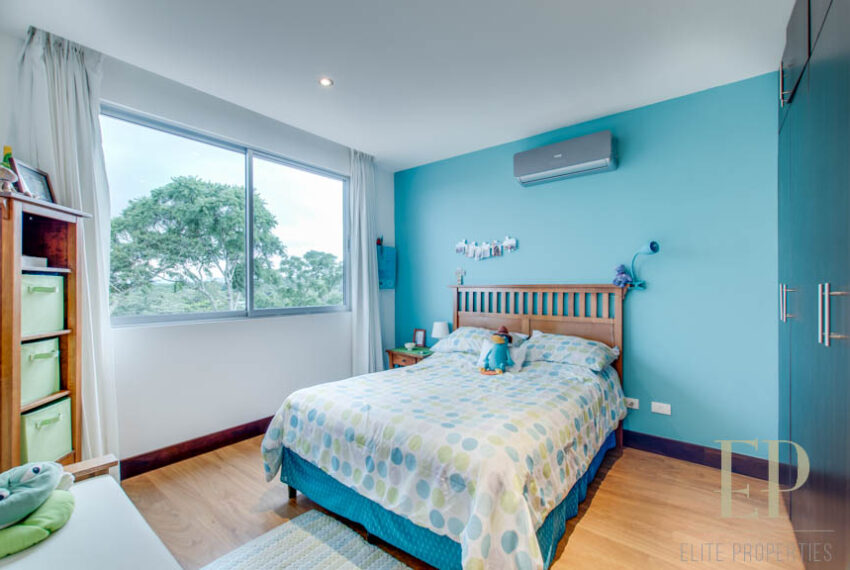
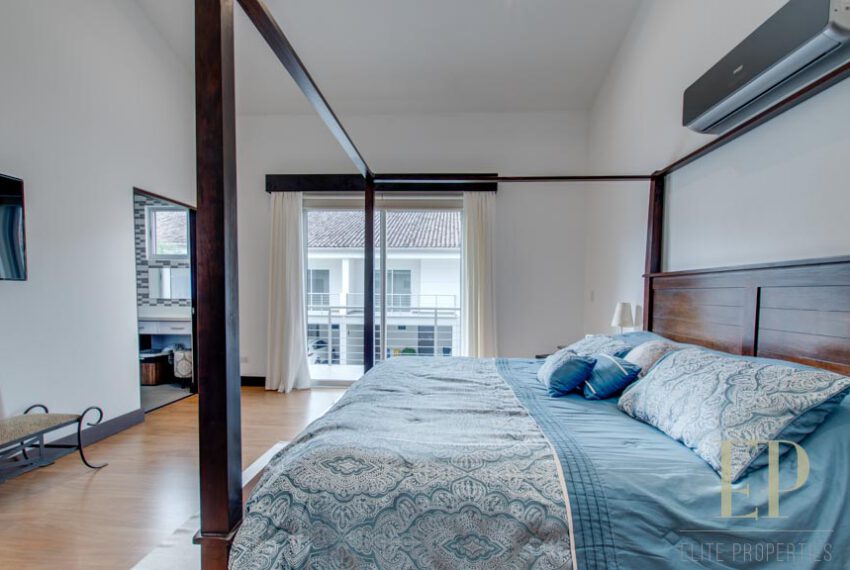
Second floor: 3 bedrooms with two bathrooms and a TV room. Master bedroom with walk in closet and bathroom, balcony and high ceiling.
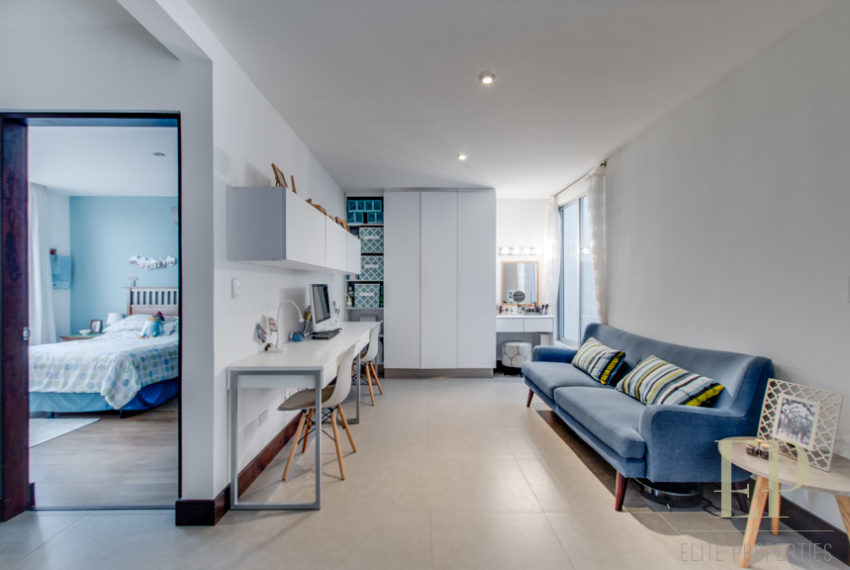
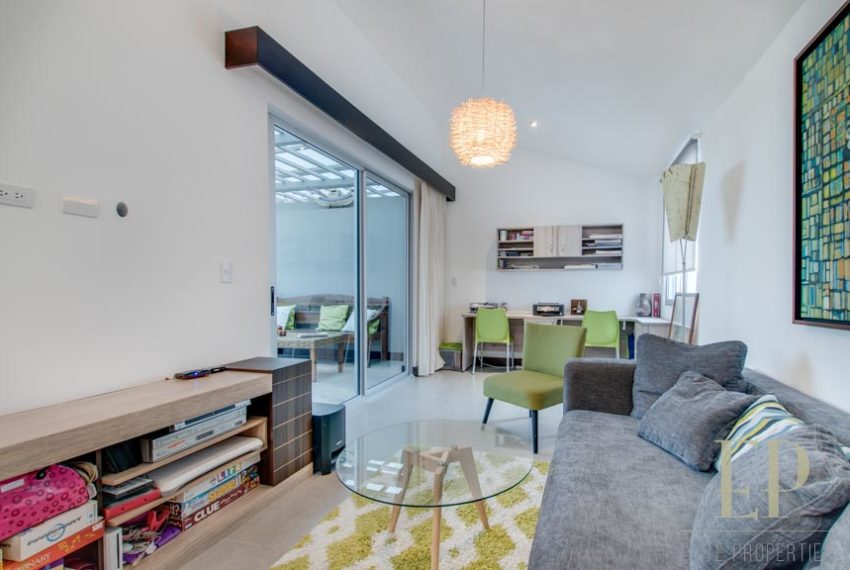
Third floor is an office/family room with terrace and more views!
Construction: 365 m2
Lot: 204 m2
Maintenance fee: 180,000 colones
For sale: $510,000
CASA CONTEMPORANA CON AMPLIA TERRAZA Y PATIO TRASERO.
Ubicada en Escazu, Jaboncillo, uno de los barrios más prestigiosos. Condominio con piscina, gimnasio, seguridad 24/7. Esta hermosa casa tiene no solo una de las mejores vistas en el condominio sino también muchos upgrades.
Espacios de gabinetes adicionales, almacenamiento, instalación de gas, aire acondicionado en las habitaciones, doble lavabo en el baño principal.
TRES NIVELES CONTIENEN: Primer piso: amplia sala de estar, comedor con cocina abierta, cómoda terraza y patio verde con vistas. Cuarto de servicio con baño, garaje para 3 autos, baño de visitas. Segundo piso: 3 habitaciones con dos baños y una sala de televisión. Dormitorio principal con walk in closet y baño, balcón y techo alto. El tercer piso es una oficina / sala familiar con terraza y más vistas.
Cuota de mantenimiento: 180,000 colones
En venta: $ 510,000
photos Lighthouse Studio
Welcome to Escazu Costa Rica. Central Valley region
San Jose suburb is located on a hill about five miles west of the downtown San José area.
This is a great city to live in with modern amenities. Upscale yet charming, Escazú dates back to colonial times and is a favorite destination for well-to-do international travelers and expatriates. US ambassador has his home here in Escazu.
You’ll find here movie theaters, top restaurants, supermarkets, private schools, gyms, spa, private hospitals, tennis courts and 18-hole golf course at the country club. Shopping fans will enjoy Escazú’s large mall that has three floors, plenty of international brands, restaurants and coffee shops. Farmer’s market can be visited in Escazu Centro every week.
Escazu real estate market offers variety of properties. Land, apartments, condos, houses and luxury villas. Lots of development and properties to choose from.
Beach is only 1h 30 min away.
Nature lovers will enjoy here many great hiking trails in San Antonio Escazu as well as in Santa Ana mountains. We recommend to try Pico Blanco and Crus de Alajuelita hike.
Bienvenido a Escazú en el Valle Central, Costa Rica. El suburbio de San José está ubicado en una colina a unas cinco millas al oeste del área del centro de San José.
Esta es una gran ciudad para vivir con comodidades modernas. Exclusivo pero encantador, Escazú se remonta a la época colonial y es un destino favorito para los viajeros y expatriados internacionales. El embajador de Estados Unidos tiene su casa aquí en Escazú.
Aquí encontrará cine, los mejores restaurantes, supermercados, escuelas privadas, gimnasios, spa, hospitales privados, canchas de tenis y un campo de golf de 18 hoyos en el club de campo. Los fanáticos de las compras disfrutarán del gran centro comercial de Escazú que tiene tres pisos, muchas marcas internacionales, restaurantes y cafeterías. El mercado de agricultores se puede visitar en Escazu Centro todas las semanas.
El mercado inmobiliario de Escazú ofrece una variedad de propiedades. Terrenos, apartamentos, condominios, casas y villas de lujo. Mucho desarrollo y propiedades para elegir.
La playa está a solo 1 hora y 30 minutos.
Los amantes de la naturaleza disfrutarán aquí de muchas rutas de senderismo en San Antonio Escazú y en las montañas de Santa Ana. Recomendamos probar la caminata Pico Blanco y Crus de Alajuelita.















































Wehrle
hgh anti-aging dosierung
References:
Wehrle
valley.md
testosterone enanthate and dianabol cycle
References:
valley.md
swav.sa
hgh vor oder nach dem training
References:
hgh dosage for beginners (swav.sa)
easyconnect.fun
buy anabolic steroids with credit card
References:
are there legal steroids (easyconnect.fun)
Gitea.Alaindee.Net
natural steroids for muscle growth
References:
What Are Steroid (Gitea.Alaindee.Net)
https://maps.google.cat/url?q=https://www.valley.md/understanding-ipamorelin-side-effects
best place to inject cjc 1295 ipamorelin
References:
cjc-1295 ipamorelin Cost – https://maps.google.cat/url?q=https://www.valley.md/understanding-ipamorelin-side-effects –
Ipamorelin Reconstitution
can you take ipamorelin by mouth
References:
Ipamorelin Reconstitution
graph.org
what resultscan i expect from ipamorelin
References:
how do you take Cjc 1295/ ipamorelin (graph.org)
Emory
ipamorelin cjc-1295 injections
References:
ipamorelin muscle growth benefits; Emory,
git.saret.dev
how to reconstitute cjc 1295 ipamorelin 5mg
References:
cjc 1295 ipamorelin reviews (git.saret.dev)
fmagency.co.uk
can ipamorelin cause erectile dysfunction
References:
tesamorelin/ipamorelin blend dosage [fmagency.co.uk]
cjc 1295 ipamorelin before and after
cjc-1295 ipamorelin dosing protocol
References:
cjc 1295 ipamorelin before and after
hafrikplay.com
top selling muscle building supplements
References:
fda approved steroids (hafrikplay.com)
valley.md
legal steroids for sale uk
References:
valley.md
seychelleslove.com
anabolic steroids side effects pictures
References:
top Oral steroids (seychelleslove.com)
valley.md
dianabol for beginners
References:
valley.md
syq.im
best supplement stacks for getting ripped
References:
steroid abuse side effects (syq.im)
Niqnok.Com
steroids for sale online
References:
supplement stack for strength (Niqnok.Com)
https://mes-favoris.top/item/404193
best non steroid supplement for muscle growth
References:
anadrol vs dbol (https://mes-favoris.top/item/404193)
aryba.kg
legal steroids usa
References:
winstrol joint pain supplements (aryba.kg)
Https://Sfenglishlessons.Com/Members/Raingalley5/Activity/297682
best muscle pill supplements
References:
Why Do Anabolic Steroids Differ From Other Illegal Drugs (https://Sfenglishlessons.Com/Members/Raingalley5/Activity/297682)
Dixie
When To Take Anavar For Best Results Timing, Dosage, And Maximizing Benefits
Stanozolol (Stanoz – “Stano”)
What it is
Item Description
Generic name stanozolol
Brand names Stani, Zoloft (different from SSRI), Stanozol
Drug class Synthetic anabolic‑androgenic steroid (AAS) – a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Molecular formula C₁₉H₂₆N₂O₂
Key structural feature A 2,4‑diethyl substitution on the D
ring and a 17β‑OH group that confers anabolic activity.
—
How it works – Mechanism of action
Receptor binding
– Binds to intracellular androgen receptors (AR) in target
cells (muscle, bone, liver).
– The ligand–receptor complex translocates to the nucleus and dimerizes.
Gene transcription
– AR‑ligand complexes bind androgen response elements (AREs) on DNA → upregulation of genes that drive
protein synthesis (e.g., creatine kinase, glycogen synthase).
Anabolic effects
– ↑ muscle cell size and strength by increasing
amino‑acid uptake and translation.
– ↑ bone mineral density via osteoblast activation.
Metabolic modulation
– Enhances insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues → more efficient glucose uptake.
– Alters lipid metabolism, often lowering LDL cholesterol.
Interaction with other hormones
– May suppress GnRH pulse frequency → lower endogenous
testosterone.
– Can modulate estrogen receptor activity (some evidence of weak agonist effect).
—
3. Therapeutic Uses
Condition Rationale / Evidence Typical Dose
& Duration
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Improves insulin sensitivity, lowers fasting glucose, reduces HbA1c by ~0.4–0.6% 100 mg BID for 12–24 weeks
(often 200–400 mg/day)
Metabolic Syndrome / Dyslipidemia Lowers LDL-C (~10–15 mg/dL),
modestly raises HDL-C; decreases triglycerides by ~10–20 % Same as above
Pre‑diabetes & impaired fasting glucose Reduces progression to diabetes (RCTs show 25–30 %
risk reduction) 200–400 mg/day for 6–12 months
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Improves insulin sensitivity;
decreases androgen levels in some studies, but evidence
is mixed 400 mg/day may be used, though not approved for this indication
Other endocrine disorders Limited data; off‑label use reported for thyroid
dysfunction and adrenal insufficiency, but no robust
trials
> Bottom line: The strongest evidence supports Metformin’s role in type 2 diabetes and the prevention of diabetes in high‑risk individuals.
For other endocrine conditions, data are largely anecdotal or derived from small studies.
—
4. Dosing & Administration
Indication Typical Starting Dose Titration Max Daily Dose Formulations
Type 2 diabetes 500 mg PO BID (with meals) Increase by 500 mg BID every week/month
as tolerated 2000 mg/day (1000 mg BID) IR, SR, extended‑release tablets; oral solution
Prevention of type 2 diabetes (e.g., Diabetes Prevention Program) 850 mg
PO QD or 425 mg BID Titrate to 850 mg daily as tolerated 1700 mg/day
IR tablets
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) 500–1000 mg PO BID with meals (usually
for 6–12 months) Adjust dose based on ovulation and side‑effects 2000 mg/day SR tablets
Notes:
For diabetes prevention, many studies used the higher dose of 850 mg daily, which is about double the typical PCOS dose.
The lower 425 mg BID dose has similar efficacy but may
reduce GI symptoms.
When using metformin for PCOS or diabetes, it is
usually started at a low dose (e.g., 500 mg once daily) and increased gradually to reach the target dose over several weeks.
3. How Metformin Works – The Pharmacology
Target Mechanism of Action Resulting Effect
AMPK (AMP‑activated protein kinase) Metformin activates AMPK in liver,
muscle and adipose tissue. Increases fatty acid oxidation, glucose uptake, reduces gluconeogenesis.
Mitochondrial Complex I Mild inhibition of complex I decreases ATP
production, raising AMP/ATP ratio. Activates AMPK; also reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis by
limiting energy for the process.
Gluconeogenic Enzymes (PEPCK, G6Pase) Down‑regulation via AMPK and decreased cAMP signalling.
Less glucose produced by liver.
Insulin Sensitivity Improved through increased GLUT4 translocation in muscle; reduced lipid intermediates that
impair insulin signalling. Lower fasting glucose, improved OGTT results.
—
3. Clinical Implications
Situation Relevance of Metformin’s Mechanism
Type 2 Diabetes First‑line therapy; improves glycaemic control
by reducing hepatic glucose production and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
Prediabetes/Impaired Glucose Tolerance Prevents progression to diabetes, partly due to
its effects on hepatic gluconeogenesis and weight neutrality.
Metabolic Syndrome Improves fasting triglycerides, HDL‑C, and waist circumference; mechanisms
include reduced VLDL production (via lower
hepatic lipogenesis) and improved insulin signalling in adipose
tissue.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Lowers circulating androgen levels by improving insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing ovarian androgen production.
Weight Management Generally weight‑neutral; may aid modestly in appetite suppression due to increased satiety hormones.
—
4. How Metformin Works – The Biochemical Pathway
A. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex I (Complex I)
Target: NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase,
the first enzyme of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC).
Effect: Decreases proton pumping from matrix to intermembrane space → ↓ mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm)
→ ↓ ATP production.
Consequence: Cells experience an energy deficit; AMP/ATP ratio increases.
B. Activation of AMP‑Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)
Energy Sensing:
– ↑ AMP binds to AMPK γ subunit → conformational change.
Phosphorylation & Activation:
– LKB1 phosphorylates Thr172 on the α catalytic subunit → full activation.
Downstream Targets:
– Liver: Inhibits ACC → ↓ malonyl‑CoA → ↑ fatty acid
oxidation; inhibits HMG‑CoA reductase
→ ↓ cholesterol synthesis.
– Glucose Metabolism: Enhances GLUT4 translocation to plasma membrane → ↑ glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue.
– mTORC1 Inhibition: AMPK phosphorylates Raptor (Ser792) →
suppression of mTORC1 signaling, reducing protein synthesis.
2.2 Inhibition of ACC
Mechanism: In the liver, insulin activates SREBP‑1c, which upregulates ACC expression. Inhibition reduces
malonyl‑CoA, relieving inhibition on CPT‑1 and promoting fatty acid
oxidation.
Outcome: Decreases hepatic triglyceride synthesis, lowering VLDL
secretion.
2.3 Downstream Metabolic Effects
Process Effect of Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Glucose uptake (muscle) ↑
Glycogen synthesis (liver) ↑
De Novo lipogenesis ↓
Triglyceride assembly (VLDL) ↓
LDL‑R expression ↑
Clearance of LDL particles ↑
HDL‑C levels ↑ (via reverse cholesterol transport)
These changes shift the lipid profile from an atherogenic pattern (↑ TG, ↓ HDL‑C,
↑ small dense LDL) toward a protective pattern (↓ TG, ↑ HDL‑C, more large buoyant LDL).
—
3. Clinical Implications & Practical Recommendations
Goal Target Values Key Actions
Body weight / BMI 40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) women; >50 mg/dL men Moderate exercise, moderate
alcohol, healthy fats
LDL cholesterol 800 mg Ca/day and ~600–800 IU vitamin D daily (or via supplements if needed).
Energy: Total calories per day range from 2 200 to 2 400 kcal,
meeting the required surplus (~300 kcal) for muscle
gain while avoiding excessive fat.
> Note: If you are vegan or have dietary restrictions, substitute dairy with fortified
plant milks and use tofu, tempeh, seitan, lentils, chickpeas,
quinoa, nuts, seeds, and fortified nutritional yeast to meet protein and calcium needs.
3️⃣ The Power of Progressive Overload (How To Lift More)
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of muscle growth.
It means consistently challenging your muscles by gradually increasing the stimulus—be it weight, volume, or intensity—so that the body adapts with larger, stronger
fibers.
Method What It Means When to Use It
Increase Load (Weight) Add 2–5 lb each rep set when you can complete all
reps comfortably. Every 1–2 weeks if your lifts feel easy.
Add Reps Increase the number of repetitions per set while keeping weight constant.
When you hit a plateau on weight but still want more volume.
Add Sets Add an extra set at the end of each exercise.
For beginners needing to build overall volume without
heavy loads.
Reduce Rest Time Shorten rest between sets by 5–10 sec.
To increase metabolic stress and endurance.
Change Tempo Slow down eccentric (lowering) phase or pause at the bottom.
Introduces new stimulus; good for hypertrophy.
Progress Tracking
Weekly Log: Write down weight, reps, sets, RPE (Rate of Perceived Exertion), how you feel.
Check-in Every 4–6 Weeks: Evaluate strength increases and
adjust program accordingly.
3️⃣ Sample 12‑Week Structured Plan
Below is a simple template that blends compound lifts with accessory
work. Feel free to adapt the rep ranges or exercises to match your preferences,
equipment availability, or recovery needs.
Week Day 1 – Upper Body (Push) Day 2 – Lower Body
(Pull/Glutes) Day 3 – Rest / Active Recovery
1–4 Bench Press 5×5 + Overhead Press 3×8 + Dips 3×10 Deadlift 5×5 + Bulgarian Split Squat 3×8 each leg
+ Hip Thrust 4×12 Light cardio, stretching
5–8 Incline Dumbbell Press 5×5 + Lateral Raises 4×15 + Triceps Rope Pushdown 4×12 Sumo Deadlift
5×5 + Step-Ups 3×10 each leg + Glute Bridge 4×15 Core workout, mobility
9–12 Close-Grip Bench Press 5×5 + Overhead Press 4×8 +
Dips (weighted if possible) Stiff-Legged Deadlift 5×5 + Bulgarian Split Squat 3×10 each leg + Hip Thrust 4×12
Advanced strength and hypertrophy
—
Key Principles to Maximize Gains
Principle How It Helps Practical Tip
Progressive Overload Builds muscle by gradually increasing demand.
Add 5 lb every week if you can complete all reps with good form.
Volume & Frequency Muscle adapts to a combination of sets, reps, and how often it’s hit.
Aim for ~15–20 total sets per body part weekly.
Compound Movements First Activate most muscle fibers; efficient use of time.
Start with squats or deadlifts before accessory work.
Recovery & Nutrition Muscle growth occurs outside the gym;
protein & sleep are critical. Consume 0.8–1 g/kg bodyweight protein, get 7–9 hrs sleep nightly.
Progressive Overload Continuous challenge prevents plateaus.
Add weight or reps every 2–4 weeks if possible.
—
Quick‑Start Routine (3‑Day Split)
| Day | Main Lift | Accessory
| Accessory #2 | Accessory #3 | Notes |
|—–|———–|————–|————–|————–|——-|
| Monday | Squat (or Deadlift) | Bench Press | Bent‑Over Row | Overhead Press | 5×5 for main lift, 4×8 for accessories.
|
| Wednesday | Bench Press | Incline DB Press | Seated Cable Row
| Triceps Pushdown | 5×5 / 4×10. |
| Friday | Deadlift (or Power Clean) | Pull‑Up or Lat Pulldown | Face
Pulls | Bicep Curl | 3×5 for main lift, 4×12 for
accessories. |
Warm up with light cardio and dynamic stretches.
Use progressive overload: increase weight by 2–5% every week if you can complete all reps.
3. What to Eat
Goal: Provide enough calories & protein to support muscle growth while keeping fat gain minimal.
Calorie Target
Maintenance Calories ≈ 15–16 kcal per
pound of body weight.
– For a 170‑lb individual: ~2,550 kcal/day.
Add 250–350 kcal for a modest surplus → 2,800–3,
000 kcal/day.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Nutrient % of Total Calories Daily Amount (g)
Protein 30% ~210 g
Carbs 50% ~350 g
Fats 20% ~78 g
Protein: 1.2–1.5 g per pound of body weight (≈1.5 lb ≈ 0.7 kg → 210 g).
Sample Meal Plan
Breakfast
– 3 whole eggs + 4 egg whites
– 1 cup oatmeal with berries
– 1 tbsp almond butter
Snack
– Greek yogurt (200 g) with honey & sliced almonds
Lunch
– Grilled chicken breast (6 oz)
– Brown rice (1 cup cooked)
– Steamed broccoli, olive oil drizzle
Pre‑Workout Snack
– Banana + whey protein shake (1 scoop)
Post‑Workout Meal
– Turkey sandwich: whole‑grain bread, turkey breast (4 oz),
lettuce, tomato, mustard
– Sweet potato fries (baked)
Dinner
– Baked salmon (6 oz)
– Quinoa (½ cup cooked)
– Mixed greens salad with vinaigrette
Evening Snack
– Greek yogurt (1 cup) with honey & almonds
3. Portion Sizes and Caloric Needs
Food Group Typical Serving Size Approximate Calories
Protein (chicken, turkey, fish) 4 oz (~113 g) ~120–140 kcal
Lean Beef 3 oz ~150 kcal
Eggs 1 large ~70 kcal
Dairy (milk, yogurt) 1 cup ~100–150 kcal
Whole Grains (brown rice, quinoa) ½ cup cooked ~110–120
kcal
Vegetables 1 cup raw or ½ cup cooked ~25–50 kcal
Fruits 1 medium apple ~95 kcal
Healthy Fats (olive oil, nuts) 1 tbsp olive oil ~120
kcal
> Note: These values are approximate and can vary by brand, preparation method, and portion size.
They provide a starting point for meal planning.
—
3. Designing a Balanced Meal Plan
Principles of Balance
Macronutrient Distribution: Aim for roughly 45–65 %
carbohydrates, 10–35 % protein, and 20–35 % fat per day.
Micronutrient Adequacy: Include foods rich in calcium (milk, cheese),
iron (red meat, beans), vitamin D (fatty fish, fortified milk), and potassium (bananas, potatoes).
Fiber Intake: Target 25–30 g of fiber daily to support gut
health.
Calorie Needs: Adjust based on age, sex, activity level, and goals.
Sample Daily Menu
Meal Food Items Portion Approx. Calories
Breakfast Scrambled eggs (2) + whole‑grain toast (1 slice) + sliced avocado
(½ medium) + orange juice (½ cup) 1 serving ~450
Mid‑morning Snack Greek yogurt (6 oz) + mixed berries
(½ cup) + chia seeds (1 tbsp) 1 serving ~200
Lunch Grilled chicken breast (4 oz) + quinoa (½ cup cooked) + roasted mixed vegetables (1 cup)
+ olive oil vinaigrette (1 tsp olive oil) 1 serving ~500
Afternoon Snack Hummus (2 tbsp) + carrot & cucumber sticks (1 cup total) 1 serving
~150
Dinner Baked salmon (4 oz) + sweet potato mash (½ medium) + steamed broccoli (1 cup)
1 serving ~450
Evening Treat Dark chocolate square (1 oz,
at least 70% cacao) 1 serving ~200
Total Calories: Approximately 2,950 kcal
—
how to make anabolic steroids at home (Dixie) This Plan Supports the 7‑Day Goal
Element Impact on Weight Loss
Calorie deficit (~500–700 kcal/day) Promotes gradual
fat loss (~0.5–1 lb per week) while preserving muscle mass
High protein (≈30 % of calories) Supports satiety, protects lean body mass during
caloric restriction
Balanced fats and carbs Provides energy for workouts and recovery without excessive insulin spikes
Consistent meal timing Helps maintain stable blood glucose levels, reducing cravings
—
Final Thoughts
Keep it realistic: A single “diet” is less effective than a sustainable eating pattern.
Track progress: Use food logs or apps to stay accountable; adjust portion sizes if needed.
Pair with training: Strength workouts combined with cardio will maximize
fat loss and improve overall fitness.
Good luck on your journey—stay consistent,
hydrate well, and listen to your body!
feniciaett.com
how many bodybuilders use steroids
References:
animal steroids bodybuilding (feniciaett.com)
images.google.bg
bodybuilding pills
References:
images.google.bg
https://motionentrance.edu.np/
ibuy steroids
References:
https://motionentrance.edu.np/
ipamorelin side effects men
Ipamorelin and CJC‑1295 are both peptide hormones that stimulate
growth hormone secretion, but they differ in structure, potency, duration of action, and side effect profiles.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for anyone considering their
use, whether for medical therapy or athletic performance enhancement.
What Is Ipamorelin?
Ipamorelin is a synthetic hexapeptide that mimics the natural growth hormone‑releasing hormone (GHRH).
It selectively binds to the GHSR1a receptor on pituitary somatotrophs, triggering the release of endogenous growth hormone.
Unlike some other GH secretagogues, ipamorelin has a very short half‑life, typically lasting only a few
hours after injection. Its high selectivity for the growth hormone pathway means it generally does not activate other hormonal systems such as cortisol or prolactin to a significant degree.
The short action of ipamorelin allows for precise control over growth hormone peaks when administered at specific times of
day. In clinical practice, ipamorelin is sometimes used in combination with CJC‑1295 to achieve both
immediate and sustained release of GH, leveraging the complementary pharmacokinetics of each peptide.
Ipamorelin vs CJC‑1295
CJC‑1295, on the other hand, is a larger, longer‑acting analog
that contains a hexapeptide motif similar to GHRH but also
includes a modified amino acid sequence that confers resistance to enzymatic degradation. This modification extends its half‑life from
minutes to several days, allowing for once‑daily
or even less frequent dosing. CJC‑1295 can be paired with
an attachment called DAC (Drug Affinity Complex) that further prolongs its presence in circulation.
Because of this extended duration, CJC‑1295 tends to produce
a more sustained elevation of circulating growth hormone and insulin‑like growth factor‑1 (IGF‑1).
Patients receiving CJC‑1295 often report increased lean body mass,
improved recovery from exercise, and enhanced sleep quality.
However, the prolonged exposure also raises the potential for side
effects that are less likely with short‑acting agents.
Side Effects of Ipamorelin
Ipamorelin is generally well tolerated, but users may experience some mild to moderate adverse
events:
Injection site reactions such as redness, itching, or swelling.
Transient headaches or dizziness following injection.
Mild fatigue or lethargy during the initial weeks of therapy.
Occasional feelings of bloating or water retention, likely due to increased GH levels affecting fluid balance.
Rarely, an increase in appetite or mild nausea can occur.
Because ipamorelin does not significantly influence prolactin or cortisol secretion, hormonal
disturbances are uncommon. Nonetheless, users should monitor for any changes in sleep patterns
or mood that might suggest a more systemic effect.
Side Effects of CJC‑1295
The side effect profile of CJC‑1295 is broader due to its sustained activity:
Injection site irritation, similar to ipamorelin but
sometimes more pronounced because of the larger peptide size.
Persistent water retention leading to edema in extremities or facial swelling.
Increased hunger and subsequent weight gain if caloric intake is
not adjusted.
Mild joint pain or arthralgia that may reflect increased collagen turnover or fluid accumulation.
Elevated IGF‑1 levels can, over long periods, raise the risk of neoplastic growth, particularly in predisposed individuals.
In rare cases, users report mood swings or mild depression, potentially linked to hormonal shifts.
Because CJC‑1295’s half‑life is prolonged, any adverse effects
tend to linger longer than those seen with ipamorelin and may require
discontinuation for resolution.
Combination Use: Ipamorelin + CJC‑1295
Many practitioners combine the two peptides to harness both immediate
and sustained GH release. The typical protocol involves a daily injection of CJC‑1295 to maintain baseline
growth hormone levels, paired with an additional ipamorelin dose timed to produce a sharp peak before sleep or
training sessions. This synergy can enhance muscle protein synthesis while minimizing overall
peptide consumption.
When used together, the side effect burden is often similar
to that of CJC‑1295 alone because the sustained component dominates
the profile. However, some users find that the ipamorelin pulse
reduces cumulative fluid retention by preventing excessive peak GH
spikes that could otherwise stimulate water reabsorption.
FAQs: Ipamorelin vs CJC‑1295
Q1: Which peptide is safer for beginners?
A1: Ipamorelin is generally considered safer due to its short
action and lower risk of prolonged side effects. Beginners
often start with ipamorelin side effects men
alone before adding CJC‑1295 if needed.
Q2: Can I use them interchangeably for muscle growth?
A2: While both stimulate GH, their kinetics differ. Ipamorelin is better for
targeted, acute boosts; CJC‑1295 provides a steady baseline.
For maximum muscle gain, a combination may be optimal.
Q3: Do they affect appetite differently?
A3: CJC‑1295 tends to increase hunger more consistently because of sustained GH/IGF‑1 elevations.
Ipamorelin’s effect on appetite is usually mild and short‑lived.
Q4: Are there any long‑term risks associated with either peptide?
A4: Long‑term use of high IGF‑1 levels from CJC‑1295 could theoretically increase
cancer risk, though definitive evidence in humans is limited.
Ipamorelin’s lower impact on IGF‑1 makes it comparatively safer for extended use.
Q5: What monitoring should I do while using these peptides?
A5: Regular blood tests to check GH, IGF‑1, prolactin, cortisol, and thyroid function are advisable.
Monitoring weight, water retention, and any changes in sleep or mood can help catch adverse effects early.
In summary, ipamorelin offers a precise, short‑acting method for stimulating growth hormone with minimal
side effects, while CJC‑1295 provides sustained GH release
that can yield greater anabolic benefits but carries a higher risk of fluid retention, increased appetite, and
long‑term hormonal changes. Combining the two peptides allows users
to balance immediate spikes with a steady baseline, potentially maximizing therapeutic or performance outcomes while keeping adverse events
manageable.
https://www.instapaper.com/p/16984540
steroid use in bodybuilding
References:
https://www.instapaper.com/p/16984540
capsules
BPC‑157 is a synthetic peptide that has gained attention for its potential healing properties, especially in sports medicine
and recovery contexts. While many users report positive results such as accelerated tendon repair,
improved gut health, and reduced inflammation, it
is crucial to understand the side effects associated with this compound—particularly for men—and how to use it responsibly.
Below we discuss common myths versus realities, outline
safe usage practices, and explore what BPC‑157 actually
is.
What Is BPC‑157?
BPC‑157 stands for Body Protective Compound 157.
It is a partial sequence of a naturally occurring protein found in the human stomach,
specifically a 15‑amino acid peptide derived from body protection compound (BPC).
The peptide has been shown in animal studies to promote angiogenesis
(formation of new blood vessels), enhance collagen synthesis, and stimulate growth factors that help tissues heal faster.
In vitro and in vivo experiments indicate benefits for tendon,
ligament, muscle, nerve, and bone injuries, as well as potential protective effects on the gastrointestinal
tract.
Because BPC‑157 is a peptide, it does not cross the blood–brain barrier readily,
which limits central nervous system side effects but also reduces its effectiveness in treating conditions that require systemic distribution.
The peptide is typically administered via subcutaneous or intramuscular injection, and some users take oral capsules,
although absorption through the gut can be limited.
BPC‑157 Side Effects: Myths, Realities, and How to Use It
Safely
Category Myth Reality
Injection Reactions “You’ll always get a painful reaction.” Minor injection site pain or swelling
is common but usually resolves within 24–48 hours. Serious
reactions are rare when injections are done with sterile
technique.
Hormonal Imbalance “BPC‑157 will drastically alter testosterone levels.” There is
no evidence that BPC‑157 directly affects hormone production. However, some
users report mild changes in libido or energy, which may
be indirect consequences of improved recovery rather than hormonal shifts.
Allergic Response “If you’re allergic to any peptide you’ll react strongly.” Allergic reactions are possible but uncommon. A prior sensitivity to similar peptides or injection components can increase risk.
Long‑Term Safety “BPC‑157 is completely safe for lifelong use.” Long‑term data in humans are lacking.
Most studies involve short-term (weeks) administration, so prolonged
safety remains uncertain.
Interaction with Other Medications “It won’t interact with other drugs.” BPC‑157 may influence wound healing pathways
that could affect medications like anticoagulants or anti‑inflammatories.
Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised.
Real Side Effects
Injection Site Issues – Mild redness, swelling, or discomfort can occur, especially if injection technique is suboptimal.
Repeated injections at the same site may lead to scar
tissue formation.
Digestive Symptoms – Some users experience transient nausea
or mild abdominal cramps when taking oral BPC‑157 capsules, likely due to
stomach irritation before the peptide is absorbed.
Changes in Mood or Energy Levels – Anecdotal reports describe slight increases in alertness or mood elevation, possibly
linked to improved recovery and reduced pain. Conversely, some users feel fatigue if they overuse the
peptide.
Altered Blood Pressure – Rarely, a small number of participants have
reported transient changes in blood pressure during animal studies; human data are scarce but worth monitoring for
individuals with hypertension.
Allergic Reactions – Though uncommon, symptoms such as itching, hives, or
difficulty breathing could indicate an allergy to the peptide or injection excipients.
Myths vs. Realities
Myth: BPC‑157 is a “magic cure” that works
for any injury without side effects.
– Reality: It has shown promise in controlled animal studies but
lacks extensive human trials. Effectiveness varies by injury type, dosage, and individual physiology.
Myth: The peptide is entirely safe because it’s derived from a stomach protein.
– Reality: Derivation does not guarantee safety; peptides can trigger immune responses or
interfere with cellular pathways.
Myth: You can take BPC‑157 as often as you want for maximum benefit.
– Reality: Overuse may lead to diminishing returns and potential adverse effects,
especially if the body’s natural healing processes are suppressed.
How to Use It Safely
Start with a Low Dose – For men new to peptide therapy, begin with 200–300 µg per day divided into two injections (morning and evening).
Observe how your body responds before increasing.
Use Sterile Equipment – Employ fresh needles and syringes
for each injection. Follow proper hand hygiene and store the peptide
in a cool, dry place to maintain stability.
Alternate Injection Sites – Rotate between thigh, buttock,
or abdomen to avoid tissue damage and reduce scar formation.
Monitor Blood Parameters – If you have pre‑existing conditions (e.g., hypertension, diabetes), keep regular
check‑ups. Consider basic blood panels before and after a
course of therapy.
Avoid Concomitant Steroids – Combining BPC‑157 with high‑dose steroids may blunt the peptide’s
healing benefits or increase infection risk.
Follow a Structured Protocol – Many users follow a 4–8 week cycle: 2 weeks on, 1 week off, then repeat.
This pattern helps prevent tolerance and gives
your body time to recover naturally.
Stay Hydrated & Maintain Nutrition – Adequate protein intake supports tissue repair; water consumption aids in peptide distribution.
Consult a Professional – Before starting BPC‑157,
especially if you are on medication or have chronic health issues, discuss with a healthcare provider familiar
with peptide therapy.
Optimum Peak Wellness
Achieving optimum peak wellness involves balancing physical recovery with mental and metabolic health.
For men who incorporate BPC‑157 into their routine, the following complementary strategies can enhance outcomes:
Strength Training & Recovery: Structured resistance programs paired with adequate rest days help leverage BPC‑157’s tendon and ligament healing effects.
Sleep Hygiene: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night;
growth hormone release during deep sleep synergizes with peptide therapy.
Nutrition Focused on Repair: Consume lean proteins, omega‑3 fatty acids,
antioxidants (berries, leafy greens), and adequate vitamin C for collagen synthesis.
Mindfulness & Stress Management: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can impede healing.
Techniques such as meditation or progressive muscle relaxation support recovery.
Regular Medical Monitoring: Track blood markers like CRP, ESR, and
complete blood counts to ensure inflammation is controlled and no hidden issues arise.
By integrating BPC‑157 responsibly with a holistic wellness plan—encompassing training, sleep, nutrition, and stress control—men can potentially
reduce injury downtime, improve tissue resilience, and maintain high performance levels.
Always weigh the benefits against possible side effects, remain vigilant about dosage, and keep open communication with healthcare professionals to ensure safety throughout your
recovery journey.
www.mathhomeworkanswers.org
taking steroids once
References:
http://www.mathhomeworkanswers.org
www.milehighreport.com
man stack reviews
References:
http://www.milehighreport.com
docentesdeingles.ec
the use of anabolic steroids during adolescence can cause
References:
docentesdeingles.ec
git.baltimare.org
proviron steroid
References:
git.baltimare.org
csmouse.com
best stack for fat loss and muscle gain
References:
csmouse.com
tiroljobs24.at
where can you buy steroids
References:
tiroljobs24.at
https://gitea.geekelectronick.com
what type of steroids do bodybuilders use
References:
https://gitea.geekelectronick.com
https://carpleaf5.bravejournal.net/united-front-leveraging-kpv-and-bpc-to-fight-ulcerative-colitis
anabolic vs androgenic
References:
https://carpleaf5.bravejournal.net/united-front-leveraging-kpv-and-bpc-to-fight-ulcerative-colitis
https://git.atomos.io/cerysstruthers
testosterone illegal
References:
https://git.atomos.io/cerysstruthers
kpv peptide serum
Whether Or Not you’re refining your well being routine or looking for a streamlined addition to
your every day routine, KPV delivers focused, dependable supplementation you probably can trust.
For researchers seeking to purchase KPV capsules for
their research Wholesale Peptide is a reliable source for high quality assurance, regulatory compliance and scientific support.
The company’s concentrate on research applications and third get together testing standards aligns with the necessities of serious scientific research.
Research reveals that correct storage circumstances can impact the compound’s stability and effectiveness in experimental applications.
For gut irritation like colitis, research often use oral or injectable forms
to attain systemic or focused gut supply. For pores and skin conditions like psoriasis,
researchers typically use topical formulations like lotions or gels applied on to the affected area.
Due to its potential affect on immune system balance,
KPV has attracted attention in studies related to persistent inflammatory circumstances and cellular resilience.
The tripeptide capabilities via melanocortin system pathways to scale back pro-inflammatory cytokine expression.
Guarantee compliance with all applicable laws when conducting research with
this compound. At Peplogix Peptides, delight in our craftsmanship is on the coronary heart of
every thing we do. kpv peptide serum Extremely is a peppermint-flavored oral spray containing 500 mcg of a tripeptide fragment derived from α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH).
Designed in a handy liquid format, KPV Extremely provides a practical
alternative to capsule or injection-based peptide supply.
He writes analysis papers, articles and blogs
to boost consciousness and in addition has a robust interest in instructing and public speaking.
Aspiring to be a profitable heart specialist,
Kartik believes in connecting with folks on a personal degree
and is an professional in peptides. KPV is a naturally occurring peptide
inside the body whereas Pentosan is isolated
from beech trees, and it is then synthetically processed.
Due To This Fact, it’s at all times recommended to comply with skilled
advice for safe and effective results. Additionally,
like different therapeutic peptides, KPV is likely contraindicated for pregnant
or breastfeeding girls and different people with
a historical past of cancer. We space catalyst for scientific advancement,
devoted to providing the best quality peptidesthat empower
our clients to push the boundaries. For researchers seeking high-quality KPV,
Kensington Labs supplies a reliable supply devoted to precision and innovation in scientific research.
Research demonstrates lowered matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity, which
plays a role in airway transforming. KPV additionally suppresses IL-8 and eotaxin secretion, key chemokines involved in immune cell recruitment1.
Corneal epithelial wound research present complete
re-epithelialization inside 60 hours with KPV software.
This also theoretically makes KPV efficient in treating allergic reactions
as properly (8). Studies done on animals prove that KPV accelerates the method of cutaneous wound healing in addition to pores and
skin ulcers. It has also been reported to scale back scarring because of its capacity to modulate the
metabolism of collagen deposition (4).
BioLongevity Labs isn’t an outsourcing facility as defined beneath 503B
of the Federal Meals, Drug, and Beauty act. KPV promotes migration of keratinocytes and fibroblasts via modulation of collagen metabolism20.
In corneal epithelial cell cultures, KPV elevated cell viability at concentrations of
1-10 μM.
Its multifaceted properties make it a promising software for
studies on tissue restore and mobile regeneration in non-human analysis
subjects. KPV peptide (Lysine-Proline-Valine) is a tripeptide recognized
for its highly effective anti-inflammatory properties.
This peptide is of course derived from the alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH).
In managed lab settings—covering macrophage, keratinocyte, endothelial, and neural-glial models—KPV probes how cytokines, cell
migration, and barrier function interact during irritation and healing.
By strengthening the intestinal barrier and
lowering irritation within the digestive tract, it could improve nutrient absorption and promote general steadiness.
Moreover, KPV has shown potential in enhancing pores and skin repair by soothing redness, irritation, and wounds.
KPV Peptide offers a quantity of benefits that make it a priceless alternative for pure wellness assist.
One of its major strengths is its anti-inflammatory impact, which helps
calm the physique and reduce irritation caused by overactive immune responses.
Purchase KPV peptide today from Direct Peptides, your trusted source for premium peptides.
We supply a spread of formulations, including 2 mg vials, peptide
stacks, nasal sprays in 15ml and 30ml bottles, and pre-mixed peptide pens.
Designed for various research wants, researchers can easily access the exact
formulations they require. The nasal spray
format is straightforward to use, ensures exact utility, and
allows for fast absorption, making it best for exploring the peptides’ mixed benefits.
sermorelin-ipamorelin-cjc1295 buy
Although not all of these unwanted aspect effects might happen, in the occasion that they do occur they could want medical
consideration. The amount of drugs that you just take depends on the power of the
medication. Additionally, the variety of doses you take every day, the
time allowed between doses, and the length of time
you are taking the medicine depend on the medical
drawback for which you may be utilizing the medicine.
The following information includes solely the average doses of
this medication. If your dose is completely different, don’t change it until your physician tells you to take action. It is finest
to use a special place on the physique for every injection (for example,
abdomen, hip, thigh, or upper arm). To allow you to remember to do
this, you might need to maintain a report of the date
and location for every injection.
Do not use more or less of it, and don’t use it
extra usually than your physician ordered. Using an excessive amount of will improve the risk of side effects, whereas using too little could
not improve the situation. Though sure medicines shouldn’t be used together in any respect, in different instances two completely different
medicines could also be used together even when an interaction might happen. In these cases, your physician could
want to change the dose, or different precautions may be essential.
As males age, they might expertise a decline in growth hormone manufacturing, resulting in signs
corresponding to decreased muscle mass, elevated body fat,
lowered bone density, and decreased train capacity.
Sermorelin remedy is a promising solution for bettering symptoms of GH decline.
No conclusive results are recognized whether sermorelin could
yield potential advantages for adults, corresponding to to enhance pituitary perform or mimic growth hormone secretion patterns.
Ipamorelin usually reveals noticeable outcomes inside 2–4 weeks, especially for power and restoration. Sermorelin’s results might take
4–6 weeks, with sustained improvements over time.
By following correct dosing tips and consulting a healthcare supplier, the risk of unwanted aspect effects could be
minimized. Ipamorelin and Sermorelin are each peptides
that provide anti-aging advantages, with distinct characteristics that cater to different aspects of pores and skin health and total rejuvenation. Conversely, while Sermorelin additionally enhances HGH levels,
its effects might not endure as long as a end result of a shorter
half-life. This discrepancy in period can influence
the overall efficacy and dosing frequency of the 2 peptides.
Though Ipamorelin is generally considered protected, potential unwanted effects may embrace hormone
imbalances and minor injection website reactions.
They are both lengthy chain peptides that principally differ only within the number and make-up of
amino acids in the chains. Growth hormone is launched in a sequence of spurts or
pulses throughout the day. These pulses, which peak in the evening,
promote sleep, healing, train restoration, and mobile regeneration. Insert the
needle at a 45-degree angle into the subcutaneous tissue and
slowly depress the plunger to deliver the dosage.
After administering the peptide, gently withdraw the needle, apply stress to the injection website if wanted, and eliminate the used needle correctly in a sharps container.
By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of which
peptide may be the proper selection for you. Prepared to start your journey towards better hormone
levels with Sermorelin or Ipamorelin? Our educated affected person care coordinator will guide you to choose the right alternative,
clarify the process, as nicely as answer your questions. Really Feel free
to ask for extra details or help to make the only option on your wants.
The problem is that nearly all HGH treatments can result in irreversible
acromegaly. It can even end in complications over time such
as carpal tunnel syndrome, heart disease, edema, and diabetes.
It may also take longer in your body to recover from workouts, and you might experience low power unlike earlier than. That’s why SynergenX emphasizes precision dosing, ongoing
lab work, and close supplier supervision. Sermorelin is FDA-approved for sure medical makes
use of, while Ipamorelin is usually prescribed off-label for efficiency and wellness purposes.
Both Sermorelin and ipamorelin provide similar advantages however work in several methods.
Alone, either has been confirmed efficient in treating adults with low-level GHD.
There can additionally be current analysis that since they do impact completely
different receptor websites in numerous ways, there could
be some advantages available in combining the 2 therapies.
When administering these peptides subcutaneously,
it is important to ensure correct approach to maximize their effectiveness.
Low stamina could make it tough to finish demanding bodily actions,
including intercourse. Blood checks are sometimes performed every
few months to trace progress. At All Times follow your prescribing
physician’s steerage and avoid adjusting your dose
with out medical input. Along with its needed effects,
a drugs might cause some negative effects.
We may also share our suggestion for one of the best online vendor presently supplying these peptides to researchers.
But while these two peptides can have similar effects, they
work in barely other ways. All of our content material is written by
people with a robust science background, together with
medical researchers. Over months, many people report steadier
joints and fewer aches after hard periods. Monitor focus, mood, and sleep
quality in a easy journal to substantiate progress.
How do sleep, diet, and training flip a small hormone nudge into
seen results? It is imperative to provide sufferers with complete education regarding
the right administration methods and any warning indicators to be vigilant for
in the course of the therapy regimen.
Many biohackers go so far as to refer to them because the
“fountains of youth” in the peptides world. Budget and availability could play a role in the decision-making process,
particularly when contemplating the long-term use of both peptide.
Although both are usually well-tolerated, sure precautions and contraindications must be
considered when using these peptides.
References:
sermorelin-ipamorelin-cjc1295 buy
when should you take anavar before or after workout
One Other potential downside of Anavar utilization is the chance of hormonal
imbalances. Using anabolic steroids can affect the body’s
pure hormone production, and Anavar isn’t any exception. Men, particularly, can experience
decreased testosterone production with prolonged Anavar use.
It is also crucial for feminine bodybuilders to provoke their Anavar cycle with the lowest dosage and closely monitor any unwanted effects.
For males, the beneficial dosage of Anavar ranges from 20mg
to 50mg per day. It is suggested to start out with a decrease dosage and steadily increase it to reduce the
risk of unwanted effects.
In some instances, post-cycle remedy could also be needed to assist
restore normal hormone levels. Not Like many different anabolic steroids, Anavar is known for its gentle androgenic effects, making it appropriate
for numerous demographics, including girls and youngsters, under medical supervision. One of its standout features
is its capacity to enhance protein synthesis and nitrogen retention in muscles,
which aids in muscle repair and development.
Ultimately, it is determined by your private desire and how your physique reacts to it.
“Water aids in muscle recovery and helps the physique maintain homeostasis. If we even get slightly dehydrated, our methods become disrupted, and that can hinder restoration and features,” Herda stated.
“It’s greatest to contemplate a protein complement simply that—a complement to an otherwise varied and nutritious consuming pattern. It’s essential to note that Anavar should never be taken on an empty abdomen. To maximize its effects, you must contemplate consuming a pre-workout meal or snack containing carbohydrates and protein. This will present your physique with the mandatory fuel and nutrients to help your coaching session and permit Anavar to work its magic.
It is understood for its mild androgenic results and is usually used by each women and men. One of the commonest questions individuals have about Anavar is how lengthy it takes to work. Enhancing strength and endurance is another noteworthy side of Anavar’s cutting-oriented advantages. Improving users’ bodily efficiency empowers them to push via their workouts with heightened intensity and focus. This can end result in continuous progress as the physique adapts to more onerous demands and escalating challenges.
Each person’s physique reacts in another way to Oxandrolone, so outcomes can considerably vary. At All Times monitor your body, adjusting coaching and dosage accordingly beneath acceptable recommendation whereas prioritizing well being and wellbeing. Outcomes are incessantly delayed, and the timeline can alter primarily based on varied factors. Discover the power of Anavar stack mixtures and their synergistic advantages in this insightful desk. Unleash the complete potential of your health journey by strategically combining Anavar with other compounds for enhanced results. In this case, you would begin with a lower dosage of Anavar and improve it over time. As a basic rule of thumb, most Anavar cycles should be between 4 and eight weeks in length.
Its capability to advertise lean muscle mass made it a groundbreaking medication in the area of restoration and rehabilitation. Oxandrolone stands out as a preferred supplement amongst bodybuilders, and its effectiveness has been highlighted by way of numerous consumer experiences. However, as with all supplement, it’s important to proceed with warning and moderation. A thoughtful strategy will ensure that Oxandrolone not only contributes to desired muscle development, efficiency enhancement, and fat loss but also ensures a secure and manageable expertise. Person narratives and photographic evidence usually reveal a notable transformation in people who’ve used these tablets as part of their health strategy. Many women discover that their workouts turn out to be simpler, permitting them to push through harder coaching periods with greater power.
This not only enhances outcomes but additionally helps mitigate potential unwanted effects. Anadrol can additionally be commonly used by bodybuilders and athletes to help enhance muscle mass and strength. Over the years, it has turn into one of the most well-liked steroids among these teams. One of the main advantages of oxandrolone is its ability to accentuate protein synthesis in the physique. Protein synthesis is a process where the physique repairs and builds muscle tissue, bettering muscle growth and recovery. Beyond this, oxandrolone helps the body retain nitrogen, central to muscle building. This is a dry chopping stack used to boost vascularity, muscle density, and fats loss.
If you choose to use the oral form of this steroid you could be concerned about liver toxicity, when should you take anavar before or after workout to take dianabol earlier than or after workout.
Nonetheless Andriol just isn’t of the C17-aa steroid sort,
so doesn’t stress the liver like many different oral steroids do.
One of one of the best compounds to stack Tren with is Masteron, with this being a potent recomposition combination.
They will doubtless see extra visible leanness,
muscle definition, power increments, and a significant drop
in body fat. The outcomes could go so far as a redefined, athletic physique that exudes strength and health.
Anavar, sometimes mentioned beneath the generic name Oxandrolone, holds a well-deserved status as one of the
mildest anabolic steroids. Synthesized initially for medical purposes, this drug has claimed a major corner within the fitness and bodybuilding industries.
Users often put it to use to attain a well-chiseled, lean physique and protect muscle mass throughout extreme calorie deficits.
Fat Loss and Body CompositionAnavar exhibits a novel capability to promote fats loss while preserving lean muscle mass.
git.kidsrkidschina.com
Ipamorelin features as a selective ghrelin receptor agonist, primarily working on the expansion hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) pathway.
By emulating the actions of ghrelin, Ipamorelin facilitates
the release of development hormone without impacting cortisol levels.
Some people may also encounter redness, swelling, or itching at the injection website.
If any unwanted effects persist or worsen, it is advisable to hunt steering from a healthcare
skilled. Regardless Of the chance of these reactions, many customers understand the advantages of Sermorelin as
outweighing the minor discomforts. Though Ipamorelin is
mostly considered safe, potential side effects could embody hormone imbalances and minor injection website
reactions. Peptides like Sermorelin and Ipamorelin activate
the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to release
HGH, aiding in growth hormone deficiencies and offering anti-aging benefits.
High Quality sleep is important for muscle recovery
and development and can also assist to enhance temper and cognitive function.
Sermorelin would possibly assist enhance the standard of sleep, which may
help athletes get well better from their workouts and do higher in competition. Sermorelin remedy
represents a physiologically sound approach to addressing age-related hormonal adjustments.
Not Like direct hormone replacement, it actually works by optimizing the body’s present systems.
Analysis revealed in a quantity of peer-reviewed journals supports its potential advantages for certified sufferers.
The therapeutic efficacy of HGH secretagogues in enhancing heart well being outcomes underscores the necessity for
careful consideration of individual threat components and correct medical supervision during remedy
regimens. Monitoring these physical and physiological indicators is crucial
for timely intervention and management of hormone
deficiency. The precise dosing and administration of those peptides are
key elements in achieving desired therapeutic outcomes, making them useful tools in endocrinology and anti-aging medicine.
Are you seeking to increase your Human Progress Hormone levels and enhance your
total health and well-being? In this text,
we’ll discover the world of GH Secretagogues, particularly specializing in Tesamorelin and
Sermorelin. GHS medicines have been shown to advertise deeper
stages of sleep and may help sufferers achieve better relaxation and restoration.
Sermorelin could be a useful addition to testosterone substitute therapy (TRT) because it naturally promotes the
manufacturing and release of human growth hormones from your pituitary glands.
In doing so, sermorelin can help improve muscle mass, improve libido, and
improve sexual performance. Testosterone substitute
remedy goals to achieve the identical improvements, so
adding sermorelin to your TRT can help improve your overall results.
Total, Sermorelin and Tesamorelin are thought of secure and effective choices for addressing development
hormone deficiency, supporting fat loss, and preserving muscle mass.
In comparability to alternatives like synthetic growth hormone injections,
Sermorelin is usually preferred as a end result
of its extra pure method of boosting development hormone levels
without inflicting the same stage of unwanted effects. Sermorelin therapy is probably not
appropriate for everyone, and healthcare suppliers need to fastidiously consider individual
affected person elements earlier than recommending this
remedy choice. Many women expertise vital changes throughout menopause,
together with mood swings, mind fog, evening sweats, hassle
sleeping, and anxiety. These symptoms are sometimes linked to fluctuating hormone ranges, together
with a decline in progress hormone. Sermorelin therapy offers a promising
possibility for girls in search of reduction from these signs by stimulating the body’s pure production of HGH.
Elevated HGH levels can help enhance energy ranges,
metabolism, and general health, making it simpler to manage the
challenges of menopause.
During this time, your body’s repairing and constructing — it’s the inspiration of your restoration. With improved sleep, you’ll get up extra rejuvenated, your
power ranges will be greater, and you’ll be able to
deal with your subsequent workout with vigor.
This isn’t just about feeling rested; it’s about optimizing
your body’s pure restoration course of. Sermorelin is a progress hormone-releasing hormone analog that stimulates the pituitary gland to launch development hormone.
However, studies with mice suggest that ipamorelin’s
half-life is longer than sermorelin—it lasts around 2 to three hours.
A longer half-life means ipamorelin and tesamorelin might set off
progress hormone production longer than sermorelin. Unlike HGH injections—which involve immediately
injecting an artificial development hormone— peptides like sermorelin and ipamorelin stimulate the natural release of HGH hormone from the pituitary gland.
Like sermorelin, tesamorelin binds to GHRH receptors within the pituitary gland to release
growth hormone. It was designed particularly to reduce visceral (belly) fats
in folks with situations like HIV (3).
People with energetic cancers, untreated thyroid issues, or hypersensitivity to those peptides should keep away from their
use. Keep Away From unverified online sources to forestall counterfeit merchandise and potential health risks.
Get science-backed strategies to gasoline your physique, sharpen your thoughts,
and help long-term health, delivered to your inbox each Monday.
Nevertheless, the agency cites initial findings
that present that it might be used for future therapy of age-related
conditions and metabolic disorders. KPV—a comparatively new anti-inflammatory peptide—is sought out for its ability to speed up healing, curb infection, and axe continual irritation (26).
References:
git.kidsrkidschina.com
https://oke.zone/viewtopic.php?pid=1804666
muscle building drugs legal
References:
https://oke.zone/viewtopic.php?pid=1804666
https://bcstaffing.co/
buy online steroids
References:
https://bcstaffing.co/
PedsElite
If you’re a male in your late teens and early 20s who continues to be physically
growing, you’ve a better risk of opposed unwanted effects
like zits and scarring, stunted progress, stretch marks, and aged
pores and skin. It’s not uncommon for intermediate and
even some newbie steroid users to assume they’re ready to jump
into a sophisticated cycle simply because there are a few steroid
cycles beneath the belt. This is a probably grave
mistake, although – the very last thing you wish to be doing
is rushing into superior steroid use when you’re gentle on experience.
Regardless Of the potentially very powerful benefits,
Halotestin just isn’t a really extensively used steroid, and this is
mainly due to its extensive unwanted facet effects.
Nonetheless, androgenic effects are attainable in males, and the sturdy androgenic nature of this steroid makes it unsuitable for use by females.
Aggression is an actual problem with this steroid, so for
these men who are inclined to have a brief fuse, it is a steroid to avoid altogether.
To keep away from ache and irritation, rotate your injection websites
every time, and don’t inject into the same muscle with out letting it get
well. Different supplements will give you the results you want in comparability with what works for different guys, but
most people will want to take these supplements for
the entire yr. 50mg every day of Clomid (20 days total), and include half
mg per day of Arimidex, which continues for an extra week (27 days total).
Once More, comply with the 1 Vial Testosterone Cycle above and exchange the Take A Look At with Deca.
The cycle runs for under eight weeks, enough for Deca to work to its most impact.
In 2022, an estimated zero.8% of 8th graders, zero.5% of tenth graders, and
1.3% of 12th graders reported misusing anabolic steroids in the past 12 months 31.
But unlike males who will acquire little muscle with these “milder” steroids, girls will find that these
are more than powerful enough to advertise nice muscle positive aspects, together with fat loss and performance benefits.
The root cause of gynecomastia is hormonal, resulting from an imbalance of androgenic and estrogenic
action on breast tissue (201).
When used by athletes with a standard functioning thyroid
at a dose above what is naturally produced by the thyroid, the metabolism is increased,
and fats burning turns into simpler and quicker.
Cytomel (Liothyronine Sodium) can be not an anabolic steroid within the conventional sense in that it isn’t based mostly on testosterone.
As An Alternative, it is a artificial form of the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine.
This hormone is crucial to normal metabolic processes, which might trace at its potential
for chopping and fats loss. Sustanon is apparent testosterone, so you get all the advantages of that hormone as you’ll with a
single-ester product.
This is the place knowing your steroid half-lives and clearance occasions is essential.
I even have some considerations with this technique, although, primarily across the excessive danger of things going bad.
Don’t consider gear as a magic answer, having you pack on muscle
and get ripped whilst you down donuts watching Netflix all evening.
In an uncontrolled multicenter contraceptive efficacy examine, 271 males obtained 200 mg testosterone enanthate
weekly for no much less than 6 months (202). In distinction, the
prevalence of gynecomastia elevated from 7% at baseline to 19% at the
finish of an AAS cycle in the HAARLEM examine (39).
Behavioral health professionals ought to become concerned when psychological side effects are observed.
Anabolic steroids cause masculinization of females, including
hair progress or loss, enlargement of the clitoris, and deepening of the
voice. These results are not reversible, even when the drug is promptly
discontinued. In males past the age of puberty
, unwanted side effects embody increased urinary frequency, breast tenderness and enlargement, and frequent erections.
In each men and women, anabolic steroids trigger swelling
of the ft, liver issues, and abdomen upset.
The above punishments aren’t simply relevant to Dianabol but
to anabolic steroids generally, based on the Controlled Substances Act.
Testosterone plays an necessary function in male reproductive organs
and sexual operate, according to analysis, but taking testosterone by way of steroids can inhibit two other
reproductive hormones — FSH and LH. Primobolan can add up to 10 pounds of muscle while
inducing subcutaneous fat loss. Related to Anavar, Primobolan is more frequent among ladies, with fewer incidents of
virilization in our expertise. This side effect may find yourself in the
dermis (skin) showing flushed or reddish in color.
Winstrol’s results are just like Anavar’s, permitting users to
reduce fats mass while including reasonable quantities
of muscle tissue. Deca Durabolin’s weak androgenic nature,
when mixed with excessive prolactin levels, can contribute to instances
of erectile dysfunction.
Anabolic steroids are drugs that are manufactured forms of testosterone.
The technical term for these compounds is “anabolic-androgenic steroids” (AAS).
“Anabolic” refers to tissue constructing (mainly muscle), and “androgenic”
refers to a gaggle of sex hormones referred to as androgens.
“Anabolic” denotes the ability to induce protein synthesis, notably
in muscle cells. These steroids are additionally androgenic, which means that they cause adjustments characteristic of males, such
as growth of facial hair, lack of scalp hair,
deepening of the voice, skin oiliness, and aggressive behavior.
Research indicate that between 14 % and 57 p.c of nonmedical
customers develop dependence on anabolic steroids, primarily in phrases
of the muscle-altering results quite than the mood-altering effects.
Testosterone has a twin action and can be described in phrases of its androgenic and anabolic capacities.
Anavar can additionally be utilized by experienced steroid users when cutting to maximise fats loss
whereas retaining muscle tissue. It causes surges in protein synthesis and nitrogen uptake in the muscle cells, inflicting dramatic increases in muscle
dimension and strength.
Recovery is feasible, and many individuals have efficiently overcome steroid addiction. Misusing steroids
often leads to steroid use dysfunction, where you keep using regardless of dangerous consequences.
All data generated or analysed throughout this examine are included
in this printed article and its supplementary data recordsdata.
The information extraction tables comprise the total knowledge extracted from the 109 articles
included in the review. This consists of participant data,
condition requiring treatment, the therapy offered and the outcomes of treatment.
Further details on participants’ AAS use, conditions requiring remedy, the remedies offered and outcomes are supplied in Additional file
1.
References:
PedsElite
images.google.is
anabolic steroids muscle growth
References:
images.google.is
obyavlenie.ru
hgh cycle results
References:
hgh stallone (obyavlenie.ru)
https://bookmarkingworld.review/story.php?title=hgh-–-les-bienfaits-et-risques-du-melanocortine-dans-le-renforcement-musculaire
hgh fat loss before and after
References:
hgh vor dem schlafen (https://bookmarkingworld.review/story.php?title=hgh-–-les-bienfaits-et-risques-du-melanocortine-dans-le-renforcement-musculaire)
http://Www.ecccnet.com/forums/users/plowbass02
hgh kur vorher nachher
References:
wieviel mg ist eine einheit hgh (http://Www.ecccnet.com/forums/users/plowbass02)
schoolido.Lu
hgh bodybuilding dose
References:
hgh cycle bodybuilding (schoolido.Lu)
bookmarkzones.trade
hgh dosage cycle
References:
hgh daily dosage for bodybuilding (bookmarkzones.trade)
https://www.24propertyinspain.com/
recommended dosage of hgh for bodybuilding
References:
how much hgh should i inject (https://www.24propertyinspain.com/)
http://Karayaz.Ru/user/taiwansale86/
hgh female dosage
References:
är hgh lagligt – http://Karayaz.Ru/user/taiwansale86/,
May22.ru
benefits of hgh bodybuilding
References:
anavar vs hgh; May22.ru,
https://www.udrpsearch.com/user/frognet12
hgh and test cycle
References:
hgh dosage for height increase – https://www.udrpsearch.com/user/frognet12,
Holycrossconvent.Edu.Na
bodybuilding hgh cycle
References:
How Much Hgh Do Bodybuilders Take [Holycrossconvent.Edu.Na]
https://mlx.su/
hgh cycles for beginners
References:
5 iu hgh per day results (https://mlx.su/)
hedgedoc.eclair.ec-lyon.fr
hgh cutting cycle
References:
hgh sylvester stallone, hedgedoc.eclair.ec-lyon.fr,
https://ottesen-egeberg-3.blogbright.net/anavar-results-in-bodybuilding-comparing-The-earlier-than-and-after
hgh wirkungseintritt
References:
hgh einnahme zeitpunkt (https://ottesen-egeberg-3.blogbright.net/anavar-results-in-bodybuilding-comparing-The-earlier-than-and-after)
wehrle
hgh dosage for women
References:
wehrle
premiumdesignsinc.com
how much hgh should a woman take
References:
bodybuilding hgh dose [premiumdesignsinc.com]
https://ourpet.com.br
how much hgh do bodybuilders take
References:
recommended dosage of hgh for bodybuilding (https://ourpet.com.br)
https://lovebookmark.win/
winstrom steroids
References:
https://lovebookmark.win/
https://mensvault.men/story.php?title=trenbolone-cycle-guide-stacks-and-dosages-for-bulking-and-cutting
best place to buy steroids online
References:
https://mensvault.men/story.php?title=trenbolone-cycle-guide-stacks-and-dosages-for-bulking-and-cutting
https://pad.karuka.tech/5Ql1UDT2Q1adM69ymnPWPg/
steroids for height growth
References:
https://pad.karuka.tech/5Ql1UDT2Q1adM69ymnPWPg/
www.youtube.com
beginner hgh cycle
References:
hgh test cycle (http://www.youtube.com)
gamesgrom.com
hgh bulking cycle
References:
how many ml of hgh Per day, gamesgrom.com,
anantsoch.com
hgh cycle length
References:
2 iu hgh per Day results (anantsoch.com)
hangoutshelp.net
hgh testosterone stack
References:
hgh x2 gnc – hangoutshelp.net,
sciencebookmark.space
safest steroid for muscle gain
References:
sciencebookmark.space
Sundaynews.Info
how much hgh for muscle growth
References:
Hgh Bodybuilding Dosierung – Sundaynews.Info,
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/1799011/krogh-self
hgh boosters that work
References:
hgh für frauen (https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/1799011/krogh-self)
Hedge.Fachschaft.Informatik.Uni-Kl.De
testosterone and hgh
References:
Hgh Injection (Hedge.Fachschaft.Informatik.Uni-Kl.De)
masjidwasl.com
8 iu hgh per day
References:
hgh frauen vorher nachher, masjidwasl.com,
bestbizportal.com
hgh 2 iu per day
References:
john cena hgh (bestbizportal.com)
https://rockchat.com
hgh fat loss cycle
References:
how many hgh Injections Should i take – https://rockchat.com,
Http://Everest.Ooo
is 4 iu of hgh enough
References:
Hgh Versus Testosterone, http://Everest.Ooo,
https://sportpoisktv.ru
hgh wirkung bodybuilding
References:
how to take hgh for bodybuilding (https://sportpoisktv.ru)
forum.issabel.org
hgh skin before and after
References:
hgh Hormone de croissance achat (forum.issabel.org)
md.un-hack-bar.de
hgh vs trt
References:
testosterone and hgh cycle (md.un-hack-bar.de)
funch-hinrichsen-2.blogbright.net
hgh wieviel einheiten
References:
hgh vor oder Nach dem Training, funch-hinrichsen-2.blogbright.net,
https://webzine.unitedfashionforpeace.com/author/hoodcook8
hgh vs testosterone for muscle
References:
how much hgh for bodybuilding (https://webzine.unitedfashionforpeace.com/author/hoodcook8)
eskisehiruroloji.com
how much hgh should i take
References:
dosage for hgh (eskisehiruroloji.com)
duvidas.construfy.com.br
hgh & testosterone
References:
hgh dosage for beginners – duvidas.construfy.com.br,
https://ebra.ewaucu.us/
hgh dose for fat loss
References:
hgh results after 1 month (https://ebra.ewaucu.us/)